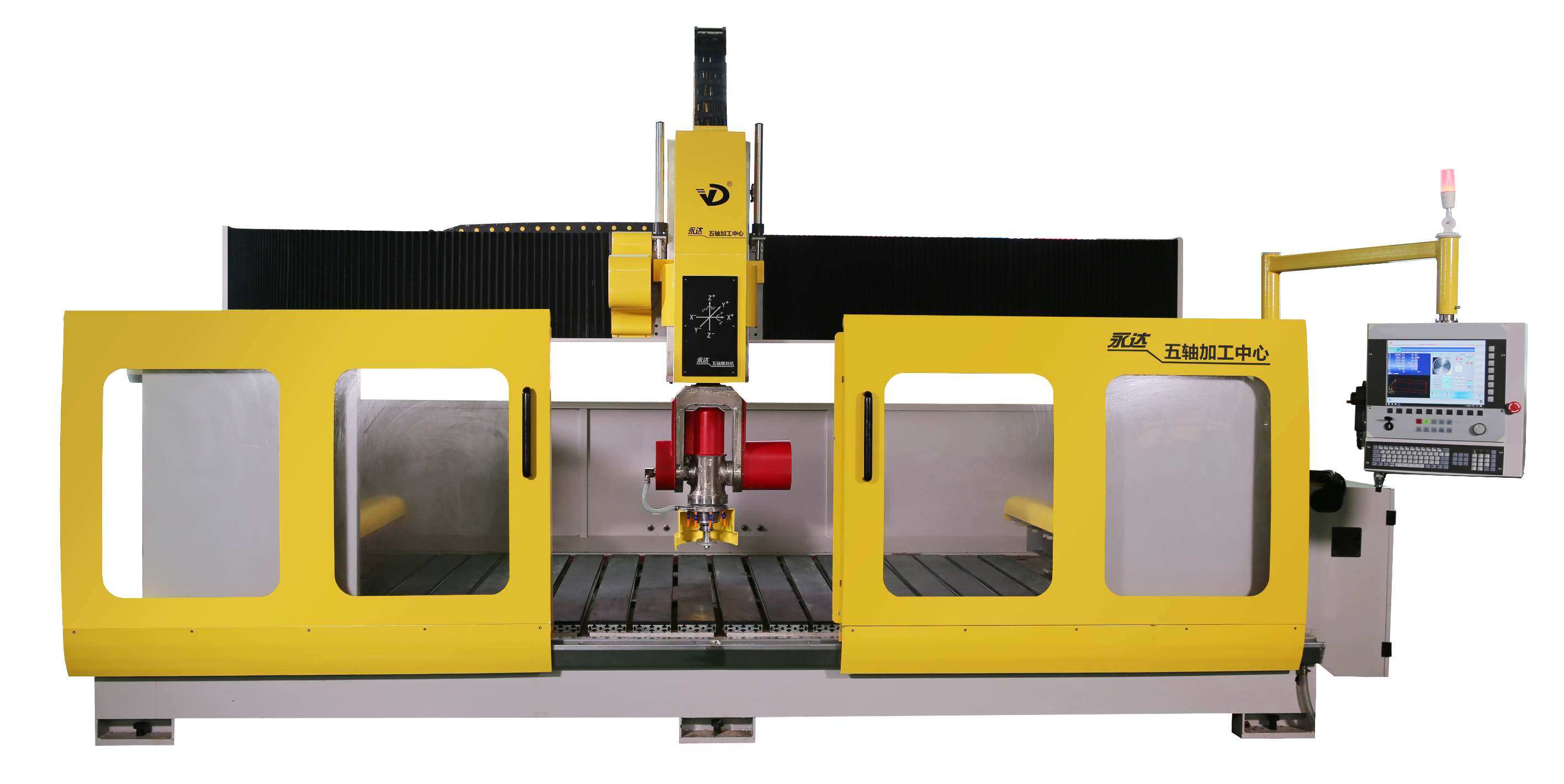
In today’s manufacturing and fabrication industries, precision and efficiency are paramount. Two widely adopted technologies—waterjet cutting machines and bridge cutting machines—play crucial roles in material processing. While they are both used in cutting operations, their mechanisms, material compatibility, and ideal use cases differ significantly.
This article explores the key differences between waterjet cutting and bridge cutting machines, including how they work, what materials they cut, their precision levels, automation capabilities, and application scenarios. By understanding these distinctions, fabricators, manufacturers, and contractors can make more informed decisions.
Working Principles
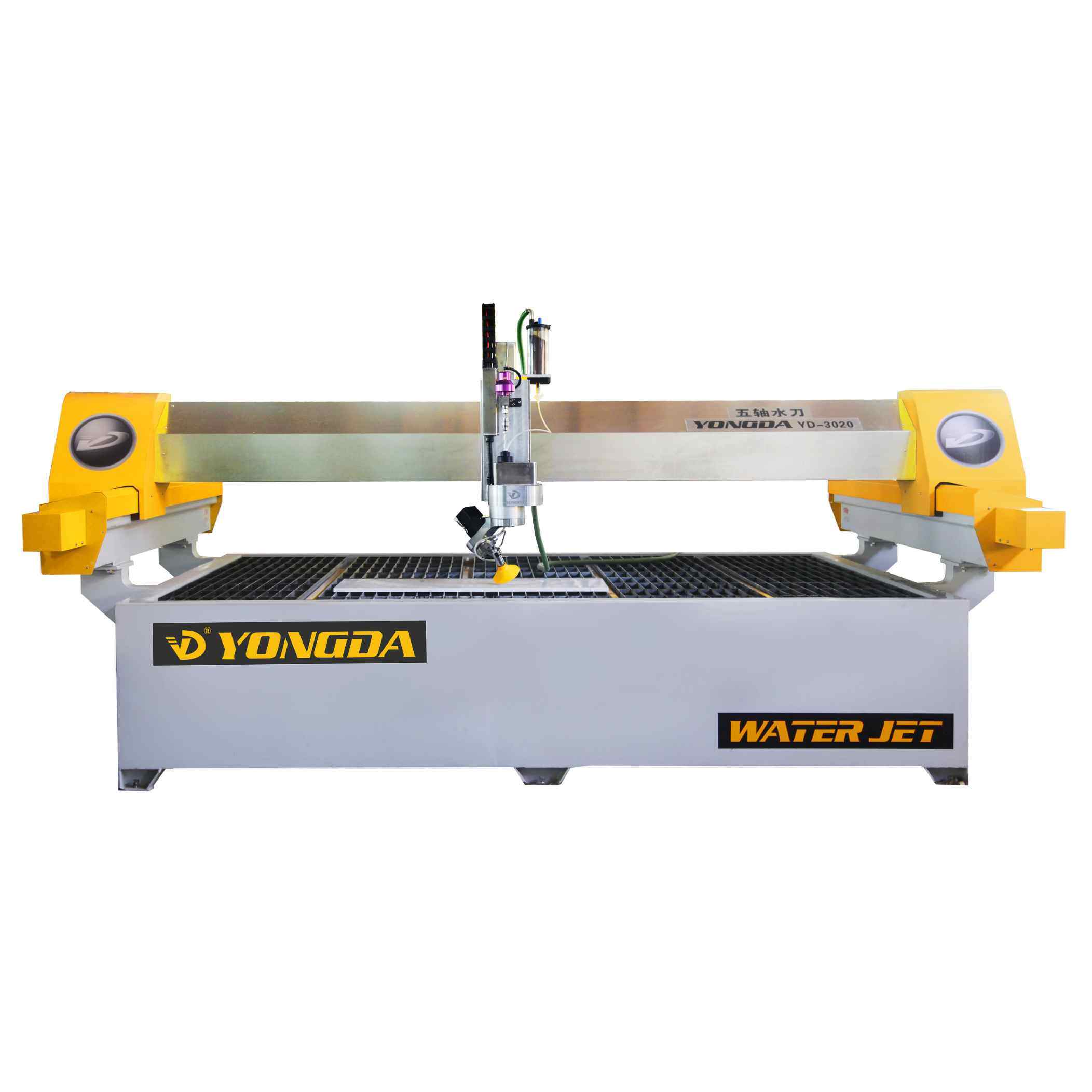
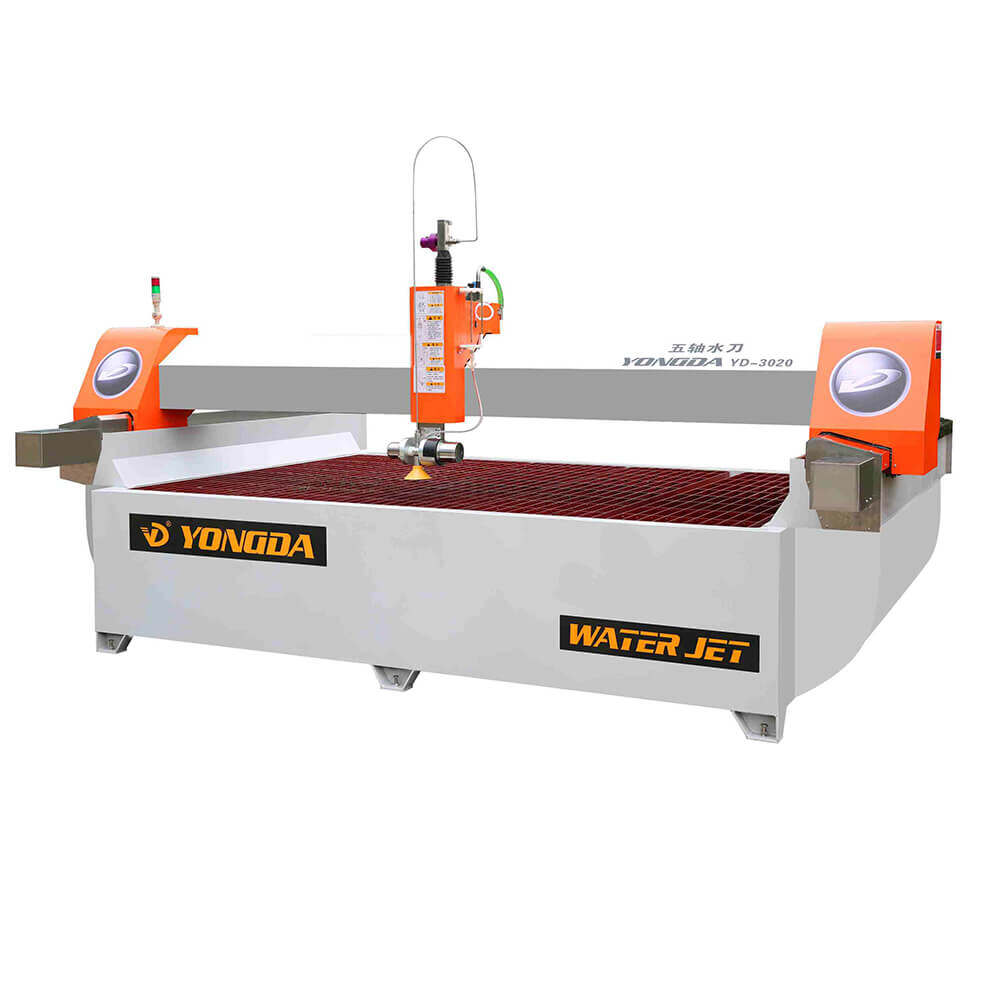
Waterjet Cutting Machine
A waterjet cutting machine uses a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive particles like garnet, to cut through a wide range of materials. The process relies on extremely high pressure (up to 60,000 psi or more), which allows the waterjet to erode the material along a pre-programmed path.
This method is a cold cutting process, which means there is no heat-affected zone (HAZ). That makes it ideal for cutting materials that could be damaged by heat, such as composites, plastics, and certain metals.
AC 5 Axis Waterjet Cutting Machine
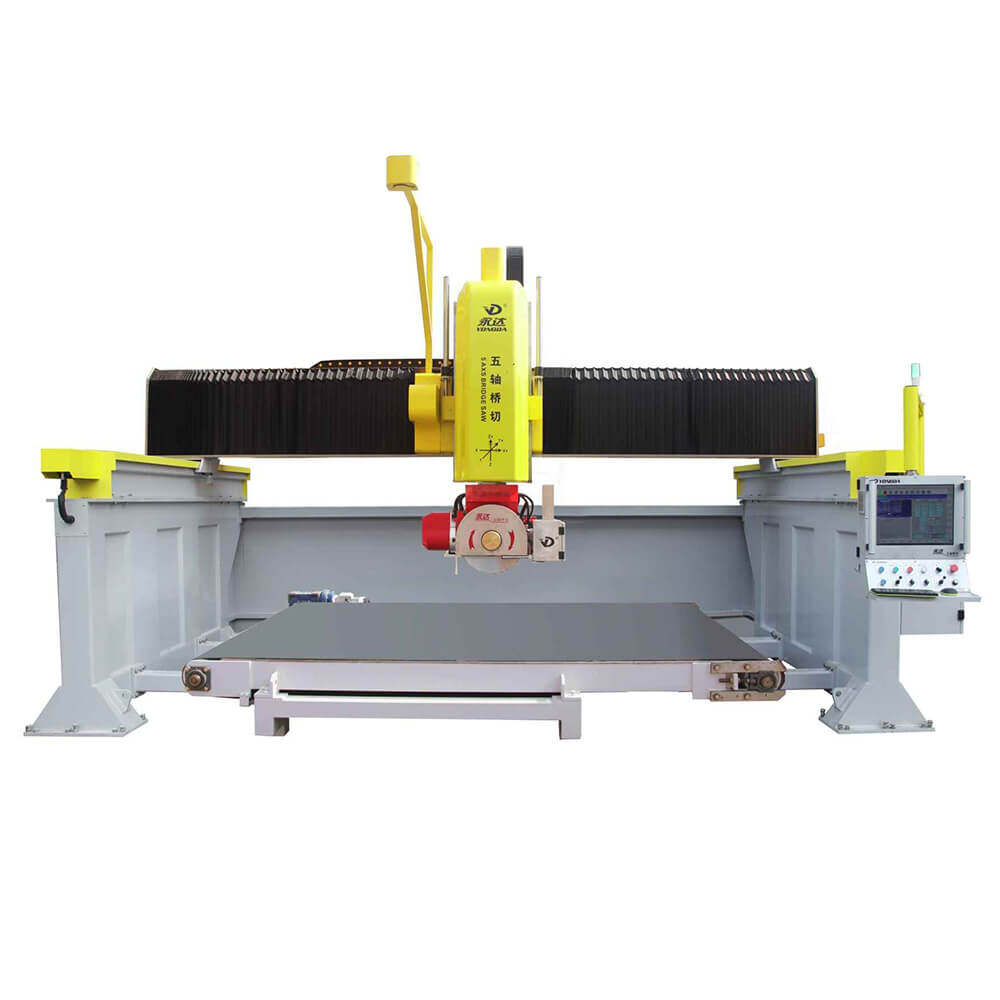
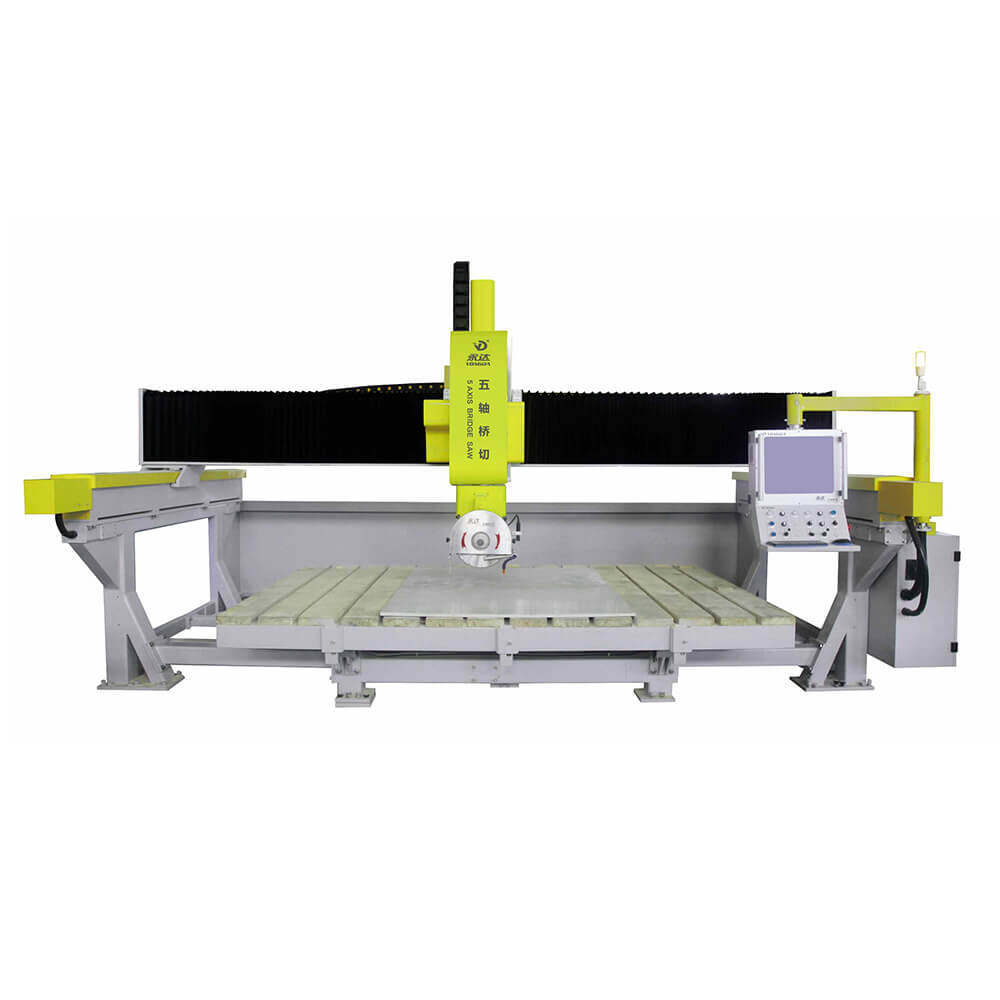
Bridge Cutting Machine
A bridge cutting machine, often referred to as a bridge saw, is typically used in the stone cutting industry. It features a diamond saw blade mounted on a movable bridge and gantry structure. The blade rotates at high speed to cut stone slabs into desired shapes and sizes.
Modern CNC bridge saws include features like automatic positioning, laser alignment, and programmable cutting paths, making them suitable for high-volume production environments.
Materials Compatibility
Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet machines can cut a wide variety of materials, including:
● Metals (steel, aluminum, copper, titanium)
● Glass (including laminated and bulletproof)
● Ceramics and porcelain
● Plastics and rubber
● Composites and foam
● Natural and engineered stone (granite, marble, quartz)
This versatility makes CNC waterjet cutting ideal for industries such as aerospace, automotive, signage, and custom architectural fabrication.
Bridge Cutting
Bridge cutting machines are generally used for:
● Natural stone (granite, marble, limestone)
● Engineered stone (quartz, sintered stone, terrazzo)
● Large ceramic or porcelain slabs
Bridge saws are most commonly found in granite countertop manufacturing, tile fabrication, and stone slab processing facilities.
Cutting Precision and Edge Quality
Precision and edge quality are important factors in choosing a cutting method.
Waterjet cutting machines offer very high accuracy, with tolerances as tight as ±0.1 mm. Since the process doesn’t involve heat, it produces clean, sharp edges ideal for parts that require tight fits or post-processing.
Bridge saw machines typically offer tolerances around ±1 mm. The quality of the cut depends on the condition of the diamond saw blade, feed rate, and operator skill. While suitable for straight and angled cuts, it’s less ideal for highly intricate patterns.
Automation and Technology Integration
Waterjet Systems
Most modern waterjet cutting machines are CNC-controlled and include features like:
● Multi-head cutting systems
● 3-axis to 5-axis capabilities
● Real-time monitoring
● Automatic toolpath generation
● CAD/CAM software integration
Manufacturers such as Yongda Waterjet offer advanced solutions for industries that require precision cutting of complex shapes.
Bridge Cutting Machines
Today’s CNC bridge saws come with robust automation features, including:
● Servo motor-driven movement
● Laser measurement systems
● Automatic cutting angle adjustment
● Digital templating
Leading brands like Yongda provide advanced systems ideal for stone fabrication shops looking to improve productivity and cut accuracy.
Operating Cost and Maintenance
Waterjet Cutting
● Higher initial investment
● Requires consumables like garnet abrasive
● Higher water and electricity consumption
● Complex maintenance (high-pressure pump, nozzles, and plumbing)
Despite the higher costs, waterjet cutting systems provide exceptional flexibility and precision, making them valuable in custom and multi-material cutting environments.
Bridge Cutting
● Lower initial and operating costs
● Diamond blade replacement is required over time
● Lower energy consumption
● Simpler maintenance routines
Bridge cutting is an economical option for high-throughput stone cutting, especially in businesses focused on countertop fabrication and large slab division.
Application Scenarios
Both machines are applicable across a variety of industries, though their strengths cater to slightly different needs. Here’s a comparison:
| Application Area | Waterjet Cutting | Bridge Cutting |
| Complex shapes and curves | ✔ | ✔ (limited) |
| Metal processing | ✔ | ✖ |
| Stone slab cutting | ✔ | ✔ |
| Ceramic and glass cutting | ✔ | ✔ (limited) |
| High precision tasks | ✔ | ✔ (depending on machine) |
| Large volume straight cuts | ✔ | ✔ |
| Heat-sensitive material processing | ✔ (cold cut) | ✖ (heat/friction involved) |
Both technologies are capable in different contexts. The best choice depends on your specific materials, design needs, and production scale.
Industry Usage Examples
Waterjet Cutting in Aerospace and Metal Fabrication
Waterjet machines are ideal for aerospace components, automotive parts, and industrial machinery, especially where tight tolerances and clean cuts are critical. Because there's no thermal distortion, waterjet systems are used for cutting titanium, aluminum, and carbon fiber.
Bridge Cutting in Stone Fabrication
Bridge saw machines dominate the stone processing industry. They are the go-to equipment in factories that cut and polish granite countertops, marble tiles, and quartz slabs. These machines provide reliable performance in high-output environments.
Summary of Key Differences
| Feature | Waterjet Cutting Machine | Bridge Cutting Machine |
| Cutting Method |
High-pressure water with abrasive (cold cutting) |
Rotating diamond blade (mechanical sawing) |
| Material Compatibility |
Metals, stone, glass, ceramics, plastics, composites |
Natural and engineered stone, large ceramic slabs |
| Precision & Complexity |
High precision, supports intricate and curved cuts |
Moderate precision, ideal for straight or angled cuts |
| Heat Impact | No heat-affected zone (cold cutting) |
Generates heat, may affect certain materials |
| Automation Options |
Advanced CNC (3- to 5-axis), CAD/CAM integration |
CNC control with laser alignment and angle setting |
| Operating Cost |
Higher (abrasives, pump maintenance, water consumption) |
Lower (simpler structure, lower power use) |
| Maintenance Requirements |
Frequent (pump, nozzle, abrasive feed system) |
Less frequent (mainly saw blade and drive systems) |
| Typical Applications |
Aerospace, metal fabrication, glass art, mixed-material parts |
Stone fabrication, countertops, tiles, building materials |
Choosing the Right Machine
When deciding between a waterjet cutting machine and a bridge cutting machine, consider:
● Material type: Multi-material vs. stone-specific
● Cutting complexity: Simple cuts vs. intricate shapes
● Volume and speed: Batch production vs. custom fabrication
● Budget and space: Total ownership cost and facility layout
Consulting with a knowledgeable manufacturer can help you match the machine to your business goals and production line requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Does waterjet cutting cause heat damage to materials?
No. Waterjet cutting is a cold process and doesn’t produce heat-affected zones, making it ideal for heat-sensitive materials.
Can a bridge cutting machine cut metal?
Generally, no. Bridge saws are designed for stone and ceramics. Metal cutting requires different blade types and equipment, such as a waterjet or laser cutter.
Is waterjet cutting environmentally friendly?
It depends. Waterjets use water and abrasive, which can generate wastewater and waste grit. However, closed-loop systems can reduce environmental impact.
Which machine is more cost-effective to maintain?
Bridge cutting machines typically have lower maintenance and operating costs. Waterjets require more frequent servicing and use costly consumables.
Which machine is better for small to medium-sized stone fabrication businesses?
Both can be suitable. Bridge saws are more budget-friendly and efficient for standard jobs, while waterjets offer flexibility for custom work across different materials.
Recommended Manufacturer: Yongda
If you’re exploring reliable cutting solutions, Yongda Machinery offers both waterjet cutting machines and bridge cutting machines tailored to various production needs.
Yongda waterjet machines are engineered for multi-material precision cutting and feature advanced CNC systems, high-pressure performance, and robust construction. These machines are perfect for cutting metal, glass, ceramic, and engineered stone.
On the other hand, the Yongda bridge saw machines deliver dependable performance in stone slab processing, with features like laser alignment, automatic angle adjustment, and smart control systems. Ideal for granite countertop manufacturers, tile fabricators, and stone workshops, these machines strike the balance between performance and affordability.
With decades of experience in manufacturing, Yongda stands as a trusted partner for businesses seeking high-quality, automated cutting technology.
Conclusion
Both waterjet and bridge cutting machines are highly effective tools for modern manufacturing. While they operate differently and serve distinct purposes, each has its advantages in terms of cutting precision, material compatibility, and cost-efficiency.
Understanding their differences allows fabricators to make informed decisions that enhance productivity and product quality.
If you’re exploring reliable cutting solutions, Yongda offers both waterjet cutting machines and bridge cutting machines tailored to various production needs. Feel free to contact us for more detailed information.