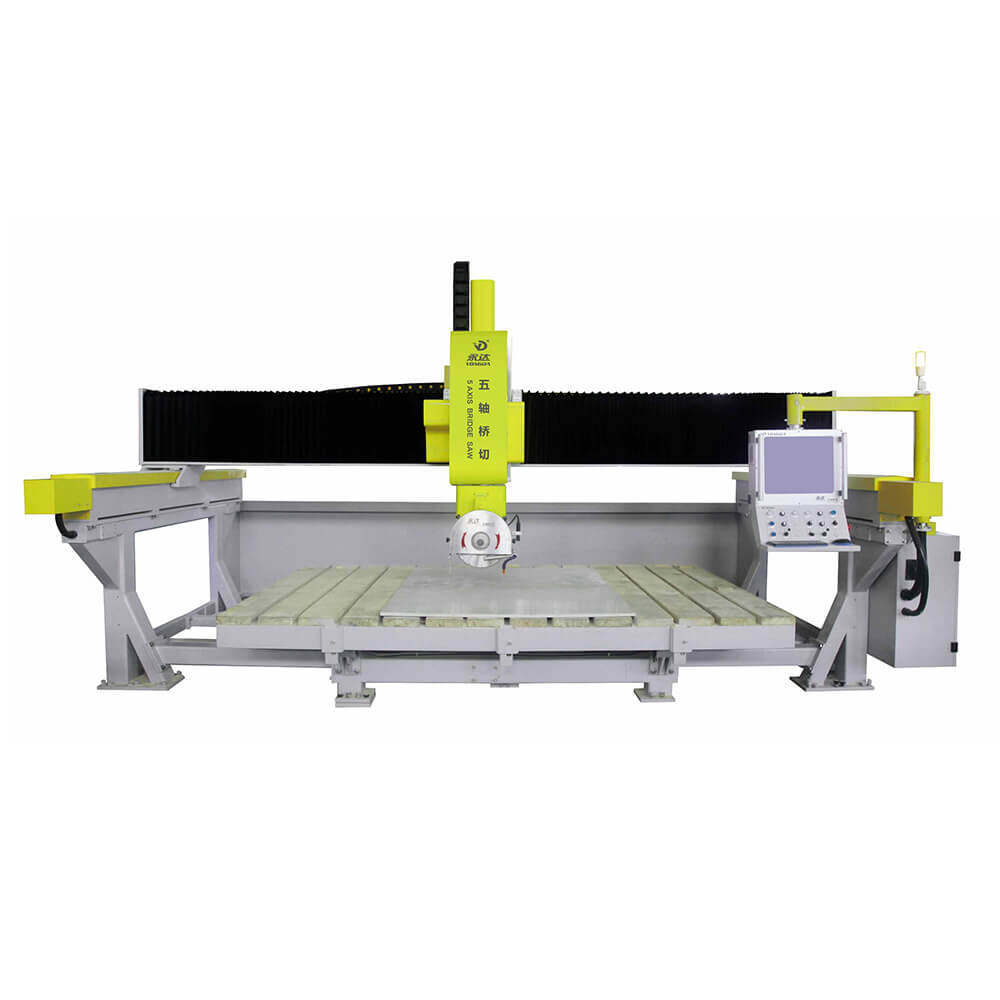
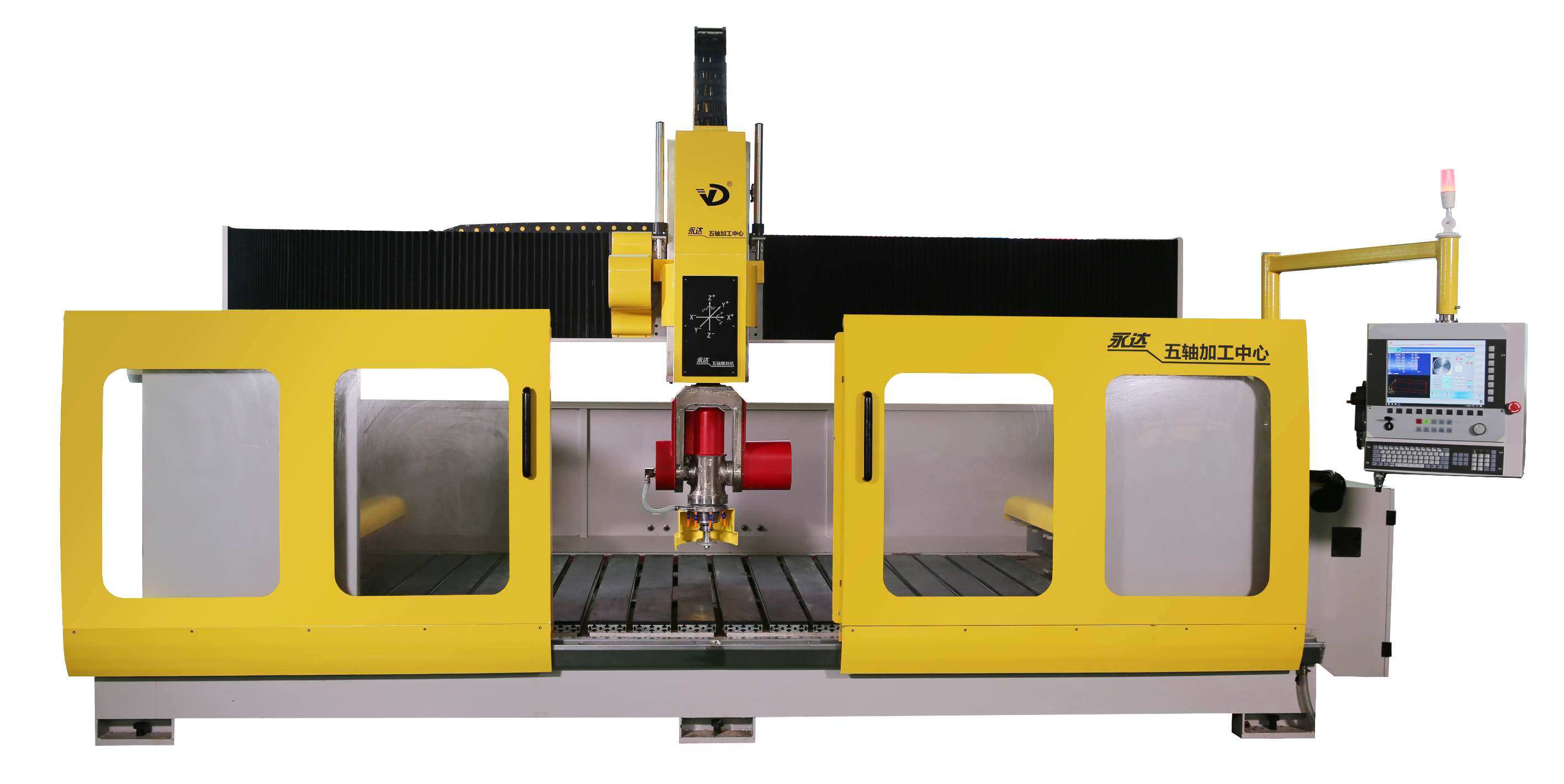
In the world of construction, architecture, and craftsmanship, precision and efficiency are essential. Stone work cutting machines serve as indispensable tools for professionals who require detailed and precise cuts on various types of stone, from marble and granite to sandstone and limestone. Whether in the creation of countertops, monuments, or decorative facades, stone cutting machines help elevate the quality and consistency of stone-based projects.
Understanding Stone Work Cutting Machines
Stone work cutting machines are specialized tools designed to cut, shape, and mold natural and artificial stones into desired shapes and sizes. These machines combine high-speed rotation, precision engineering, and various abrasive elements to achieve smooth and clean cuts. The development of these machines has changed the stoneworking industry by reducing manual labor and enabling complex designs, which were once challenging to accomplish with traditional tools.
Types of Stone Work Cutting Machines
Stone cutting machines come in various forms, each suited to different types of projects and materials. Here’s a look at the primary types:
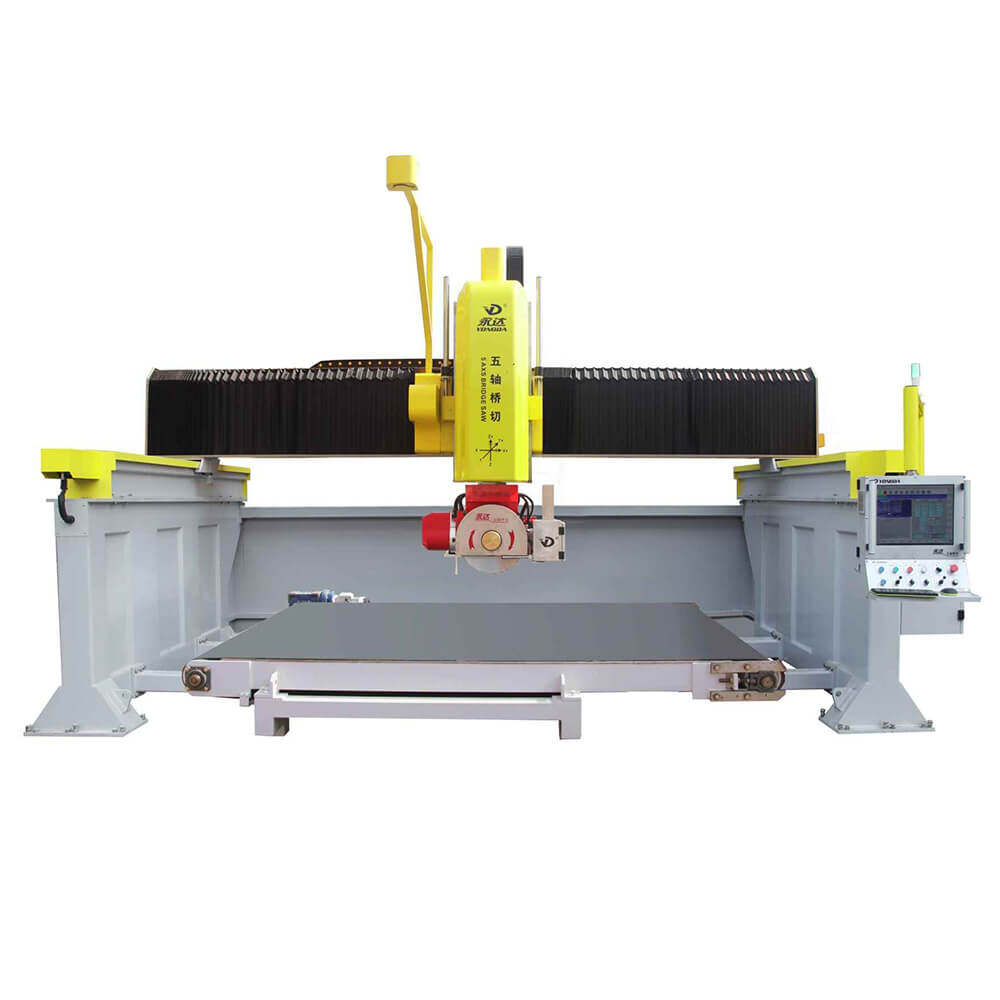
Bridge Saw Machines: A staple in stone workshops, bridge saws are designed for high-precision cuts on slabs of stone. The machine features a powerful rotating blade that moves along a bridge or rail, allowing for linear and angular cuts. This type of machine is especially popular for creating countertops, tiles, and architectural slabs.
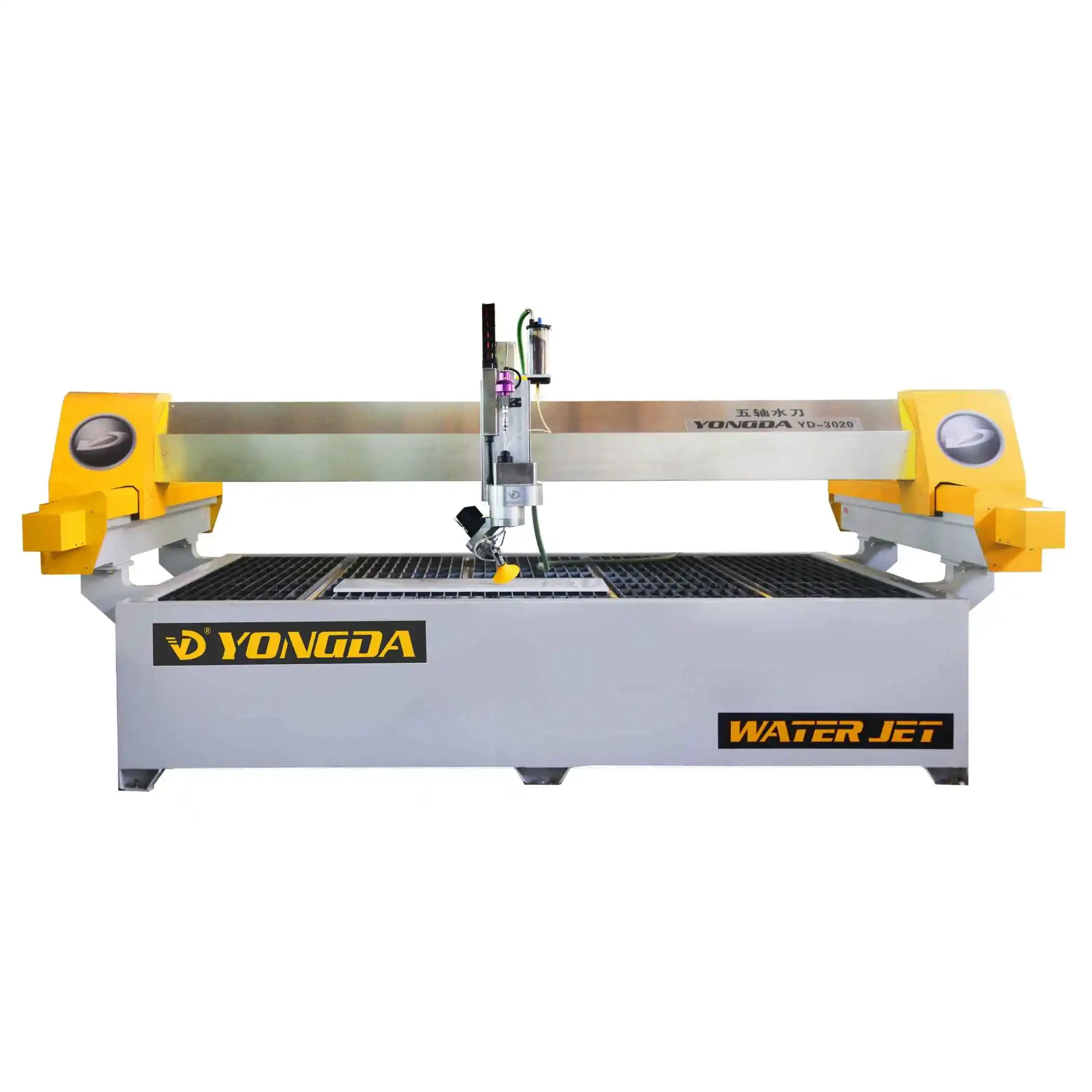
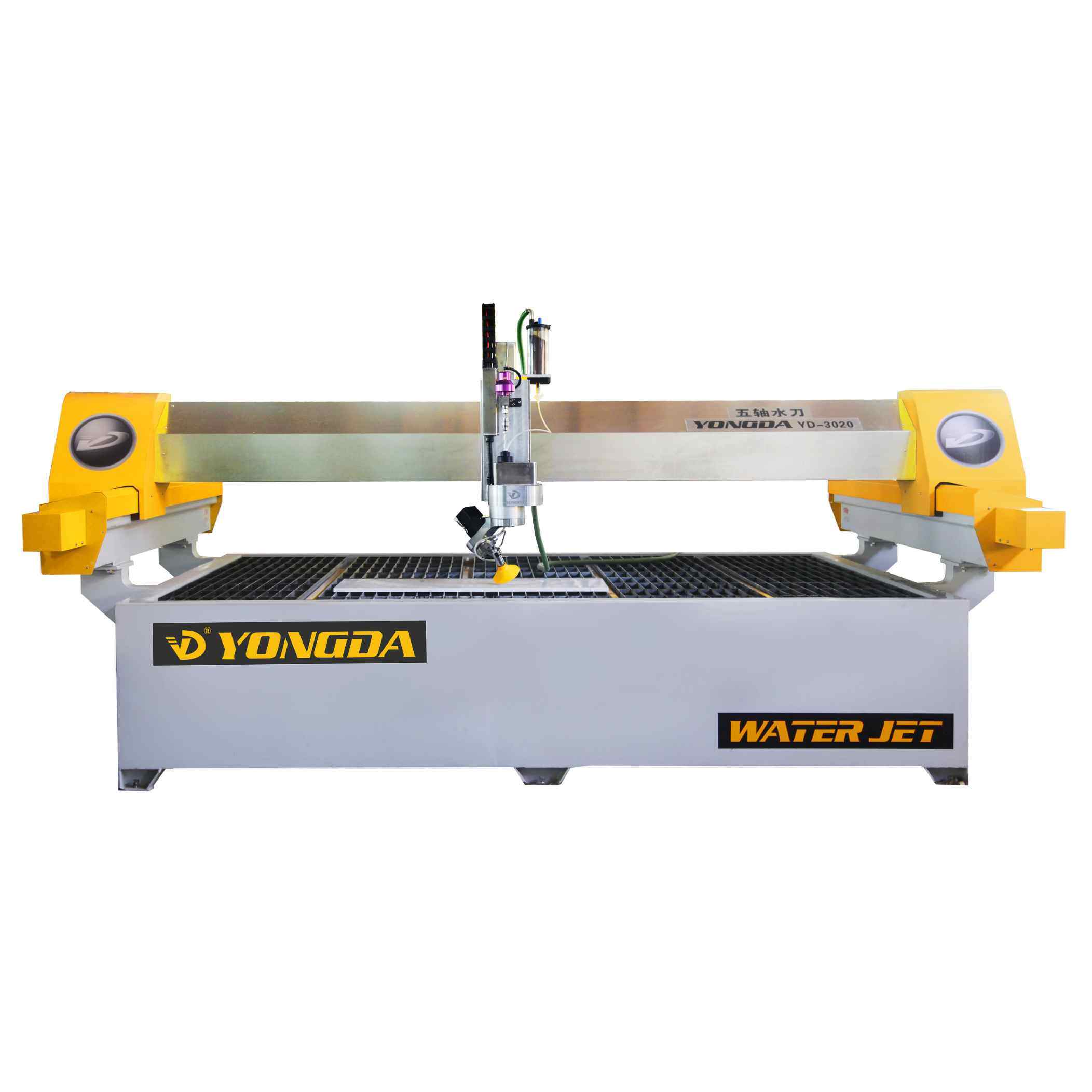
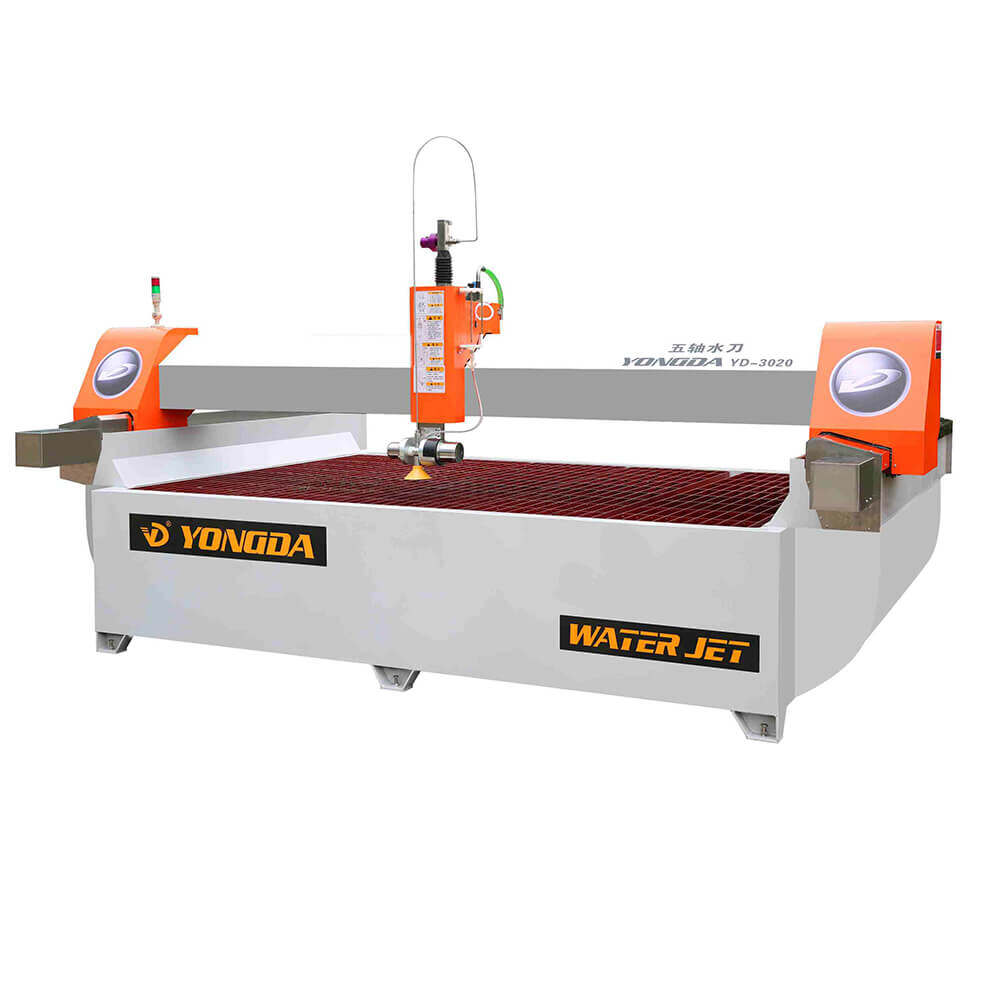
Water Jet Cutters: Water jet cutting machines use high-pressure streams of water mixed with abrasive materials, such as garnet, to cut through stones. Known for their precision and minimal heat output, water jet cutters are ideal for intricate designs and detailed cuts without causing material distortion. They are often used in artistic applications and projects requiring complex patterns.
CNC Routers: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) routers are fully automated machines that rely on pre-programmed designs to cut and engrave stones. These machines can produce highly intricate patterns and designs, making them suitable for decorative stone elements, custom engraving, and other detailed work. CNC routers are frequently used in architectural and artistic applications.
Angle Grinders: Angle grinders, though handheld, play a crucial role in stone cutting. They are often used for smaller projects and touch-up work, offering flexibility and control for detailed areas or curved cuts. Angle grinders are commonly used in the finishing stages to refine the edges of stone pieces.
Wire Saws: Wire saws use a loop of wire coated with abrasive materials to cut through larger stone blocks. These machines are often used in quarrying operations to slice large blocks into manageable sizes for transport and further processing. Wire saws are popular in the extraction of high-quality marble and granite.
Key Features of Modern Stone Work Cutting Machines
Modern stone cutting machines are equipped with advanced features that enhance accuracy, safety, and ease of use:
Automatic Positioning Systems: Many machines now come with laser guides or positioning systems that help operators achieve precise cuts. This automation minimizes waste and improves the efficiency of material usage.
Adjustable Cutting Angles: Advanced machines allow for angle adjustments, giving operators the flexibility to cut stones at different angles to suit specific design requirements.
Cooling Systems: Stone cutting generates significant heat, which can damage both the machine and the stone. Machines with built-in water cooling systems help dissipate heat and reduce dust, enhancing the longevity of the cutting tool and improving air quality in the work area.
Programmable Controls: CNC and other automated machines offer programmable control interfaces, allowing users to input specific measurements and designs. This functionality is critical for projects requiring intricate or repeated cuts.
Applications of Stone Work Cutting Machines
Stone work cutting machines are versatile and widely applicable across industries. Some of the main applications include:
Architecture and Interior Design: Stone cutting machines are instrumental in creating architectural elements such as countertops, floor tiles, and wall panels. They allow designers to achieve specific dimensions and designs that match aesthetic goals.
Monuments and Sculpture: In the field of sculpture and monument creation, precise cutting machines are essential. Artists and craftspeople use these machines to bring intricate details and unique shapes to life.
Construction: The construction industry heavily relies on stone cutting machines to prepare materials like marble, granite, and concrete for use in building structures. Machines like wire saws and bridge saws are integral to this process.
Landscaping and Exterior Design: Stone work cutting machines also play a significant role in landscaping. They are used to cut stone for pathways, retaining walls, and decorative outdoor elements, enhancing both functionality and visual appeal.
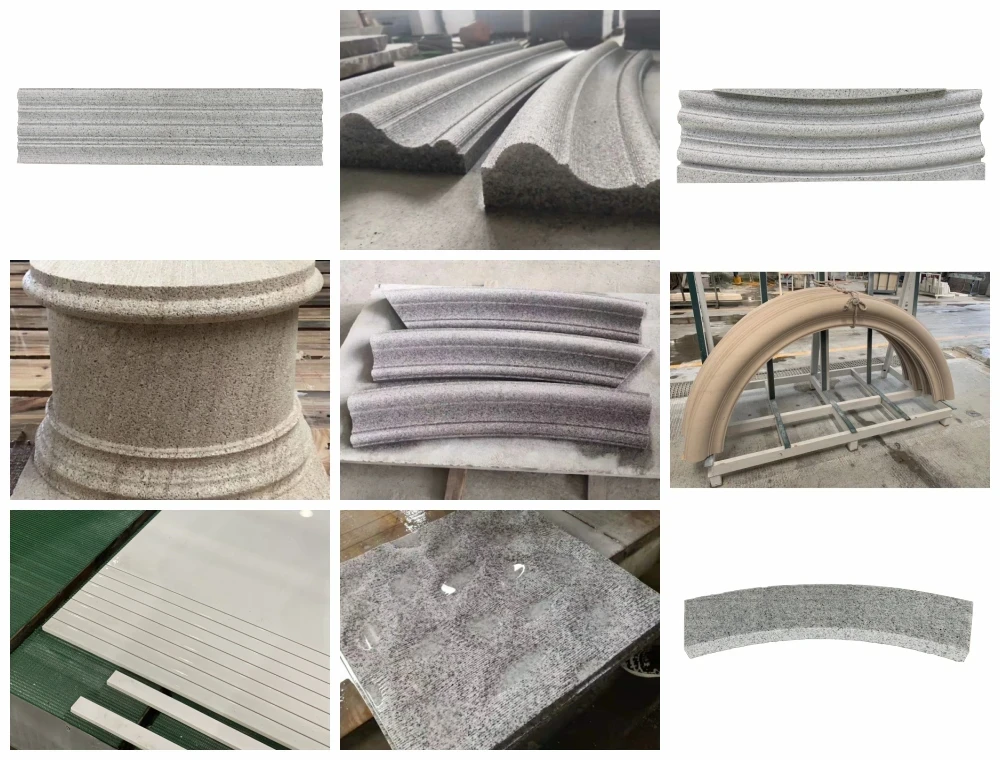

Benefits of Using Stone Work Cutting Machines
The use of stone work cutting machines offers numerous advantages that contribute to improved productivity and quality:
Enhanced Precision: Stone cutting machines can achieve a level of precision that is difficult to attain manually, ensuring that projects meet exact specifications.
Increased Efficiency: Automation and speed allow for faster project completion, reducing labor costs and enabling companies to take on more work.
Improved Safety: By mechanizing the cutting process, these machines minimize the risk of injuries associated with manual cutting, such as repetitive strain and exposure to dust.
Reduced Waste: Precision cutting reduces material waste, which is particularly important in high-cost materials like marble and granite.
Versatility: From simple to complex designs, stone cutting machines are adaptable to a wide variety of projects, making them valuable assets across multiple sectors.
Selecting the Right Stone Work Cutting Machine
Choosing the right stone work cutting machine depends on the nature of the projects and the types of stone being processed. Key factors to consider include:
Material Compatibility: Some stones are harder and more challenging to cut, requiring powerful machines with suitable abrasive capabilities.
Precision Requirements: For intricate designs, CNC routers or water jet cutters are ideal, while bridge saws work well for straight-line cutting tasks.
Budget and Project Volume: Larger operations may require high-capacity machines with advanced automation, while smaller workshops might prioritize affordability and versatility.
Conclusion
Stone work cutting machines have transformed the stoneworking industry by introducing speed, accuracy, and versatility. Their importance spans multiple industries, from architecture to art, supporting both functional and aesthetic goals. By understanding the various types, features, and applications of stone cutting machines, professionals can make informed decisions that maximize productivity and achieve high-quality results in their projects. As technology advances, these machines will continue to evolve, further expanding the possibilities for precision stonework.