Bridge saws are essential cutting machines widely used in industries like stone fabrication, construction, and metalworking. With their precision and versatility, bridge saws simplify complex cutting tasks for materials such as granite, marble, and other natural stones. While all bridge saws serve the same primary function—cutting materials with accuracy and speed—the number of axes they feature defines the scope of their capabilities. The choice between a 4-axis and a 5-axis bridge saw depends on various factors, from project complexity to budget. In this article, we’ll compare these two models to help you determine the best fit for your cutting needs.
What is a Bridge Saw?
A bridge saw is a type of industrial saw designed to make precise cuts in heavy materials, particularly in stone and construction applications. Unlike handheld or basic cutting machines, bridge saws are mounted on a bridge structure that allows the saw blade to move along multiple axes, delivering accuracy and stability. These machines are vital for tasks that require high-precision cuts, particularly in custom projects and specialized materials.
Understanding Axes in Bridge Saws
The term “axis” in bridge saws refers to the directions in which the saw blade can move. Each axis adds another level of movement or rotation, which directly influences the machine’s range of cuts. Traditional 3-axis bridge saws operate along three primary directions:
X-axis: horizontal movement across the material
Y-axis: vertical movement across the material
Z-axis: up-and-down movement (depth)
Adding more axes—such as the A-axis in 4-axis saws and both A and B axes in 5-axis saws—enhances the saw’s flexibility and versatility, allowing for more complex cutting patterns, tilts, and rotations.
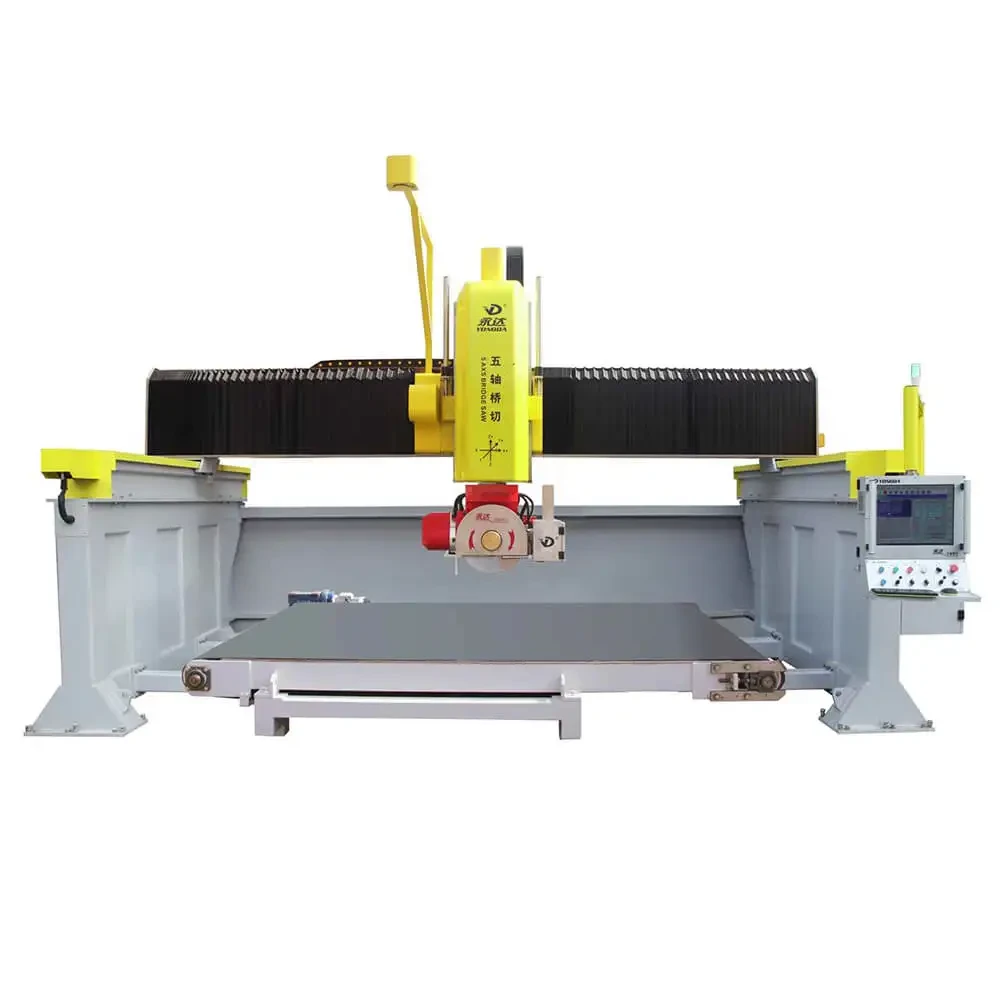
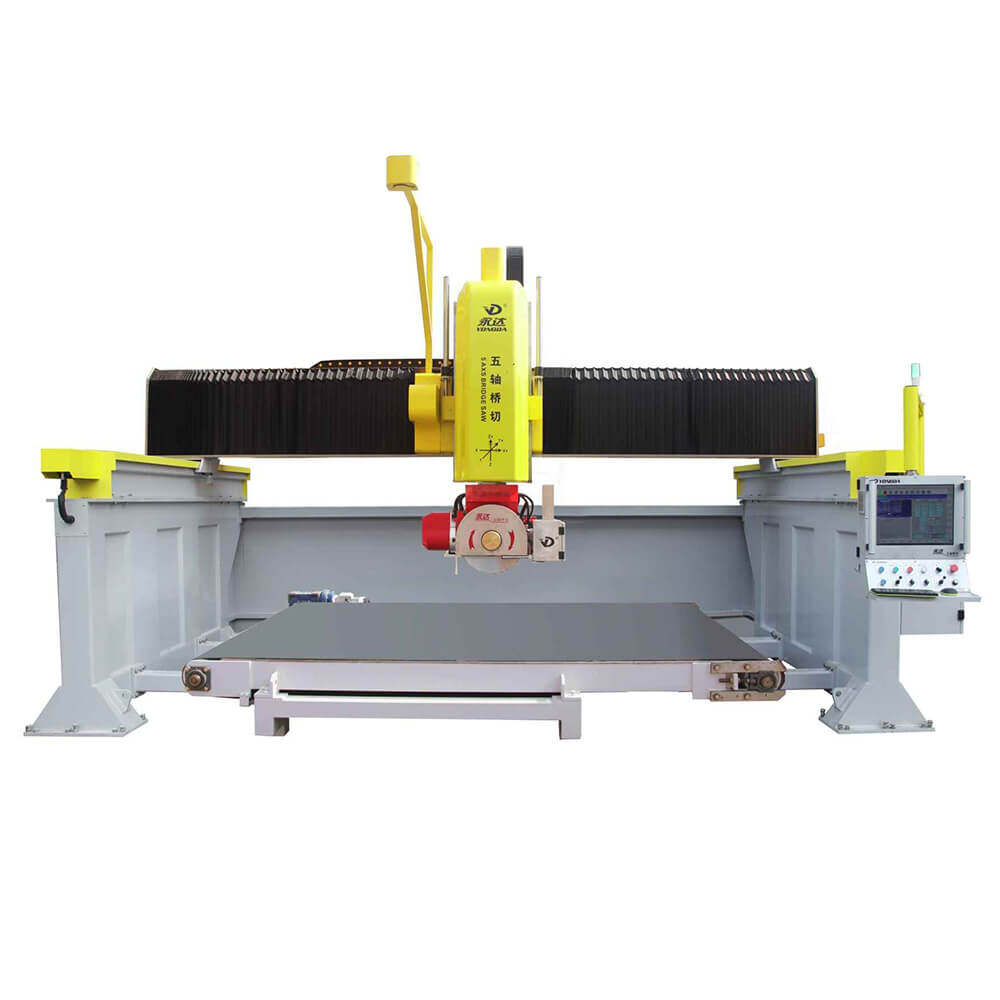
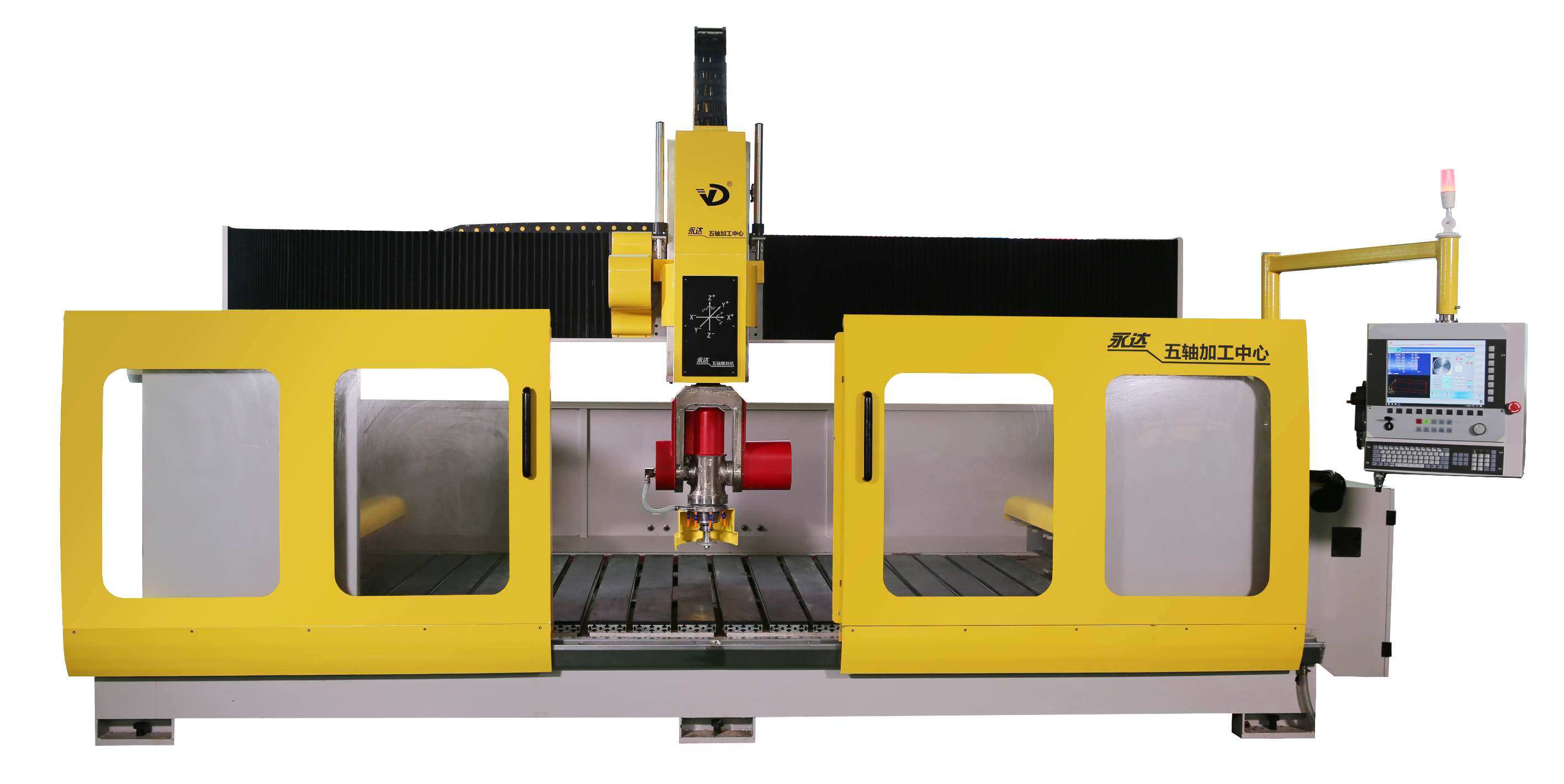
4 Axis Bridge Saw
The 4-axis bridge saw builds upon the basic three axes by introducing an additional A-axis that allows the blade to tilt, usually at angles up to 45 degrees. This enables the saw to make angled cuts, a feature particularly useful for projects that require basic beveling or slanted cuts.
Key Applications for 4-Axis Bridge Saws
4-axis bridge saws are ideal for jobs that involve:
Simple bevels and angled cuts: Perfect for creating countertop edges or sloped surfaces.
High-volume, low-complexity work: Suitable for tasks that don’t require intricate detailing.
Quick, accurate cuts: The 4-axis model is typically faster for straightforward projects, as it doesn’t involve as much setup or calibration as a 5-axis saw.
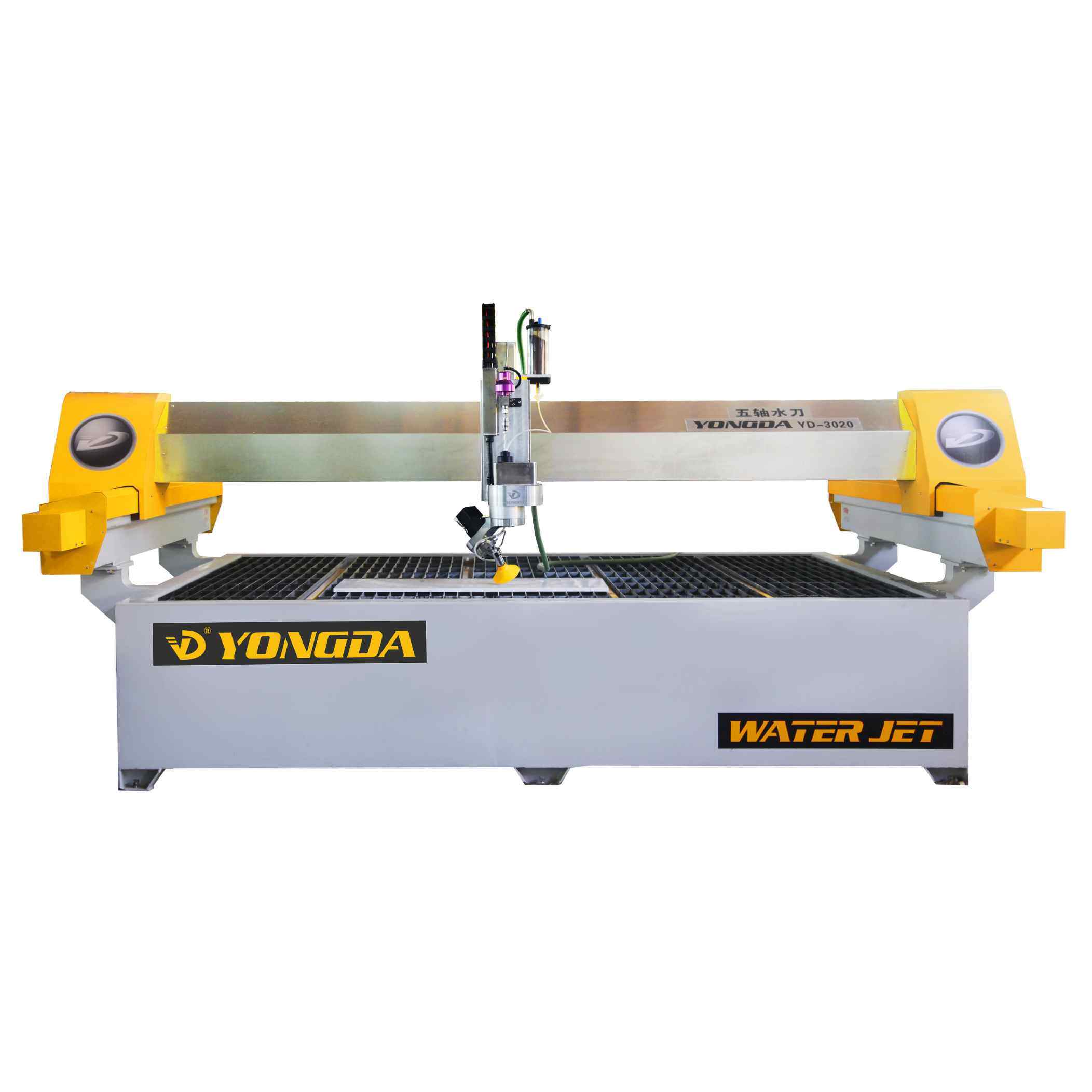
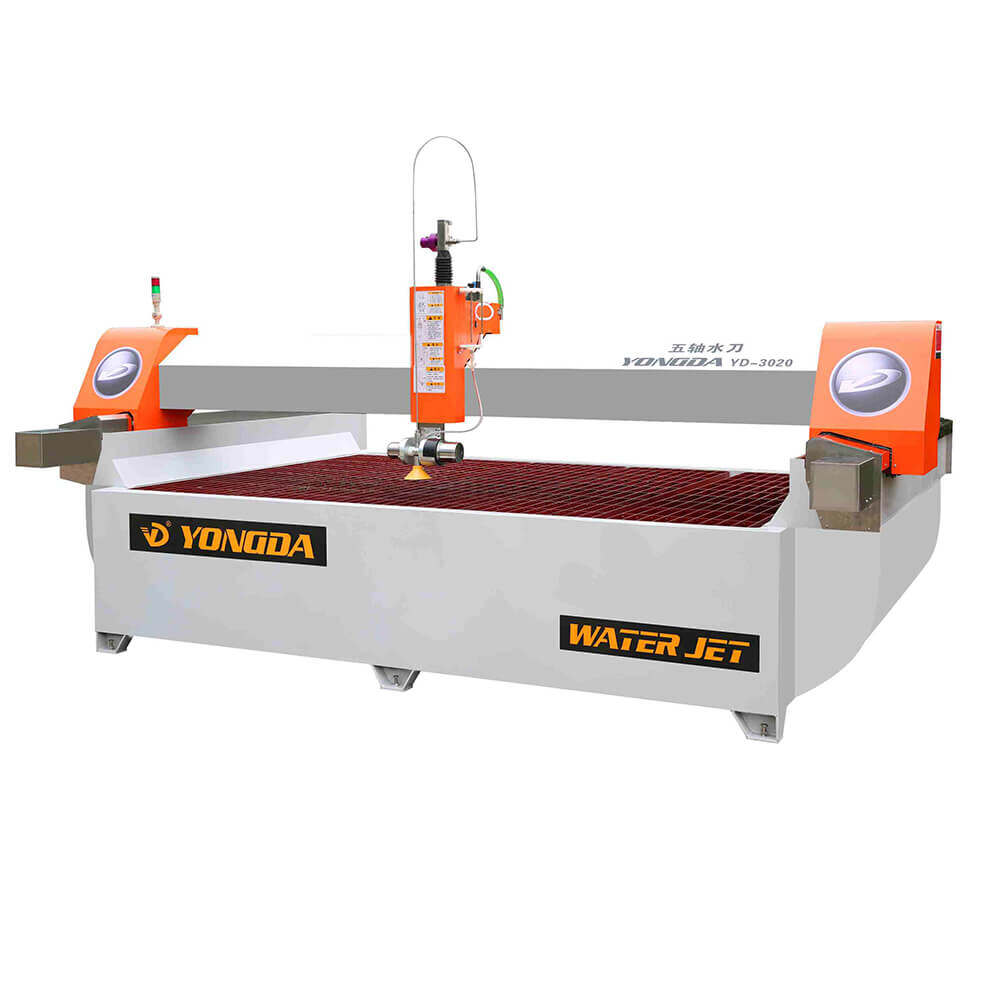
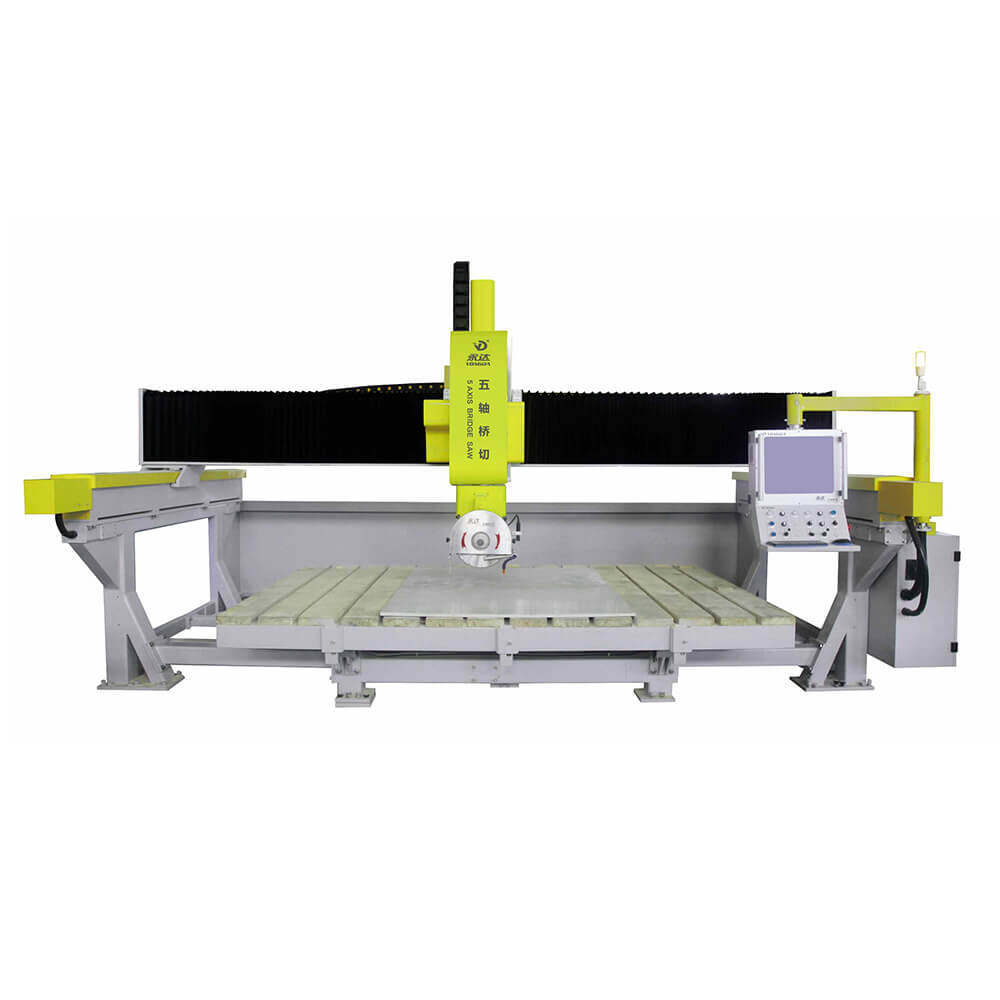
5 Axis Bridge Saw
The 5-axis bridge saw takes functionality further by adding both an A-axis (for tilt) and a B-axis (for blade rotation), enabling more intricate and multi-dimensional cutting capabilities. This additional axis allows the blade to rotate around the material, creating curves and intricate patterns that a 4-axis saw cannot achieve.
Key Applications for 5-Axis Bridge Saws
5-axis bridge saws are highly valued in specialized and custom projects, such as:
Complex stonework and sculpture: Ideal for detailed designs that require complex curves, circles, and elaborate contours.
Custom countertops and decorative pieces: The 5-axis saw allows for advanced edge shaping and intricate cuts, making it perfect for luxury or custom orders.
Multifaceted cuts in one setup: With full control over the blade’s rotation and tilt, operators can complete multiple angles and shapes without readjusting the material, increasing efficiency in detailed tasks.
Comparing 4-Axis and 5-Axis Bridge Saws
Precision and Complexity: The 5-axis saw enhanced rotational and tilting capabilities provide it with a clear advantage for precision and complexity. For high-end projects that demand intricate designs, a 5-axis saw will deliver results that a 4-axis saw cannot match.
Efficiency and Speed: While a 5-axis saw is ideal for complex cuts, a 4-axis saw is often more efficient for standard cuts. This is due to the reduced setup time and simplified operation of the 4-axis model, making it faster and more cost-effective for straightforward tasks.
Material Versatility: Both machines are compatible with a variety of materials, including marble, granite, and quartz. However, a 5-axis saw’s flexibility allows it to handle more challenging materials and shapes, giving it an edge for custom stonework and advanced applications.
Which Bridge Saw is Right for You?
Choosing between a 4-axis and 5-axis bridge saw boils down to your project needs, budget, and future goals.
For high-volume, straightforward cutting: The 4-axis saw is an economical choice that can handle most everyday fabrication needs with speed and reliability.
For custom and intricate work: A 5-axis saw is worth the investment, especially if your business demands high-end finishes, custom designs, or complex stonework.
Future-proofing: If you anticipate growing demand for custom projects, investing in a 5-axis saw may position you to take on a wider range of work in the future, making it a long-term asset for business expansion.
Conclusion
In comparing 4 axis and 5 axis bridge saws, both have valuable strengths depending on the application. While a 4-axis bridge saw offers cost efficiency and straightforward operation, the 5-axis saw brings unmatched versatility and precision for more complex projects. Carefully evaluate your project needs, budget, and technical expertise to select the machine that aligns with your goals, ensuring that your bridge saw investment maximizes both efficiency and output quality.